
Typically, a value of alpha = 0.05 is used, which corresponds to 95% confidence.

F critical will depend on alpha, which is a measure of the confidence level. A standardized table can be used to find F critical for any system. The larger the F-statistic, the more likely it is that the difference between samples is due to the factor being tested, and not just the natural variation within a group. The F-statistic is the ratio of two variance estimates: the variance between groups divided by the variance within groups. If there are non-linear relationship between these (for example, if the difference between column 1 and column 2 on the same row is that column2 = column1^2), then there is the chance that ANOVA will not catch it. ANOVA works by assuming each observation as overall mean + mean effect + noise. ANOVA will always assumes a linear model, it is important to consider strong nonlinear interactions that ANOVA may not incorporate when determining significance. Though ANOVA will tell you if factors are significantly different, it will do so according to a linear model. You want to analyze the variance of the product yield as a function of the reactor number and the catalyst concentration.

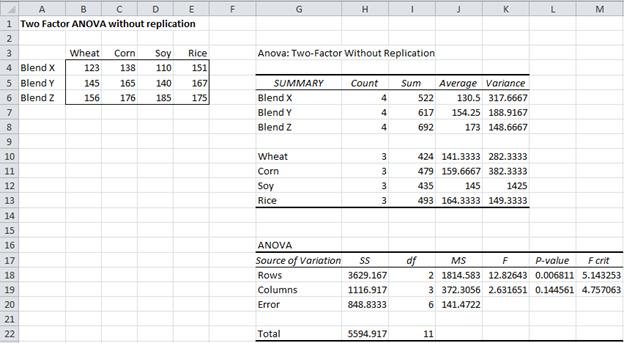
The method is highly versatile in that it can be used to analyze complicated systems, with numerous variables and factors. For example, if the P-value is low (P-value<0.05 or P-value<0.01 - this depends on desired level of significance), then there is a low probability that the two groups are the same. From this F-statistic, the P-value can be calculated to see if the difference is significant. Instead of comparing two samples, however, a variable is correlated with one or more explanatory factors, typically using the F-statistic. It is an analytical tool used to determine the significance of factors on measurements by looking at the relationship between a quantitative "response variable" and a proposed explanatory "factor." This method is similar to the process of comparing the statistical difference between two samples, in that it invokes the concept of hypothesis testing. A simple example would be using a person's intelligence (a factor) to predict their verbal, quantitative, writing, and analytical scores on the GRE (variables).Īnalysis of variance (ANOVA) is the method used to compare continuous measurements to determine if the measurements are sampled from the same or different distributions.
\( \newcommand\)įirst invented in the early 1900s by psychologist Charles Spearman, factor analysis is the process by which a complicated system of many variables is simplified by completely defining it with a smaller number of "factors." If these factors can be studied and determined, they can be used to predict the value of the variables in a system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
